“Anger is the deepest form of compassion,” poet and philosopher David Whyte wrote.
Most people do not associate anger with compassion. In fact, at first glance, it looks and feels like the exact opposite of compassion. But as with most emotions, the more attention we pay, the more aware we can be of what our anger is trying to tell us. In this article, I want to present a different take on anger – seeing anger as the most compassionate human emotion. Taking this unusual perspective about anger can reveal a lot of useful insights. Let’s get started.
On the surface, anger looks like an ugly emotion. The feeling of an intense fire that threatens to burn not just the target of the rage but also ourselves. We have all been through that. It is in those moments when we know we are going to explode, but can do very little to stop it — that we realize the energy of anger. Often we end up spending it destructively (shouting, hand waving, punching a wall).
What is Anger?
Anger is a natural human emotion. Anger is one of our most primitive biological responses, and everybody experiences it. Anger is a legitimate emotion, and there is nothing wrong with it. As my mom used to say, anger is our inability to deal with what we care about, and the vulnerability that comes along with it. We get angry when we don’t know how to react (to events around us) normally.
A lot of people see anger as a negative emotion. I wouldn’t categorize anger as negative. Instead, anger can be our guiding light. It can be a mobilization force to deploy ourselves in the face of circumstances. Every time we can do that, it strengthens and helps us behave in a way we can be proud of. Seen this way, anger is a very useful emotion.
Anger is very useful to avoid and navigate fear and threat when our survival is at stake. The human species would not have survived unless it had been for anger. I’ve never met a human being who doesn’t feel anger. Everybody gets angry at some point in their life. People might have different thresholds for anger. People might react to anger in different ways, but everyone gets angry.

Anger from Psychological Point of View
Anger is a secondary emotion. What that means is that it can hide more emotions behind it. For example, anger can hide frustration, sadness, or even grief behind it. Anger is also not a static emotion. Your anger can range from mere irritation, on the one hand, to rage on the other hand. Anger can be triggered suddenly or it can linger deep inside yourself.
Physical Manifestation of Anger
Everyone reacts differently to anger, but there are some common physiological changes associated with it. It causes our heart rate and blood pressure to go up, and we feel an adrenaline rush when we get angry. We get a sudden rush of energy and an impulse to react in a particular way – banging our fists, cursing, shouting, venting, throwing things, etc.
Anger is harmful to your health. It causes stress and anxiety, and it can cause long term harm like heart attack and depression. It is not only harmful to our own health, but it is also harmful to people around us, and our relationships. In anger, we tend to lose control, and we can do things that we might regret later. If we look back in our lives we can all see moments of anger where people have left a trail of destruction behind them.
Neuroscience Point of View
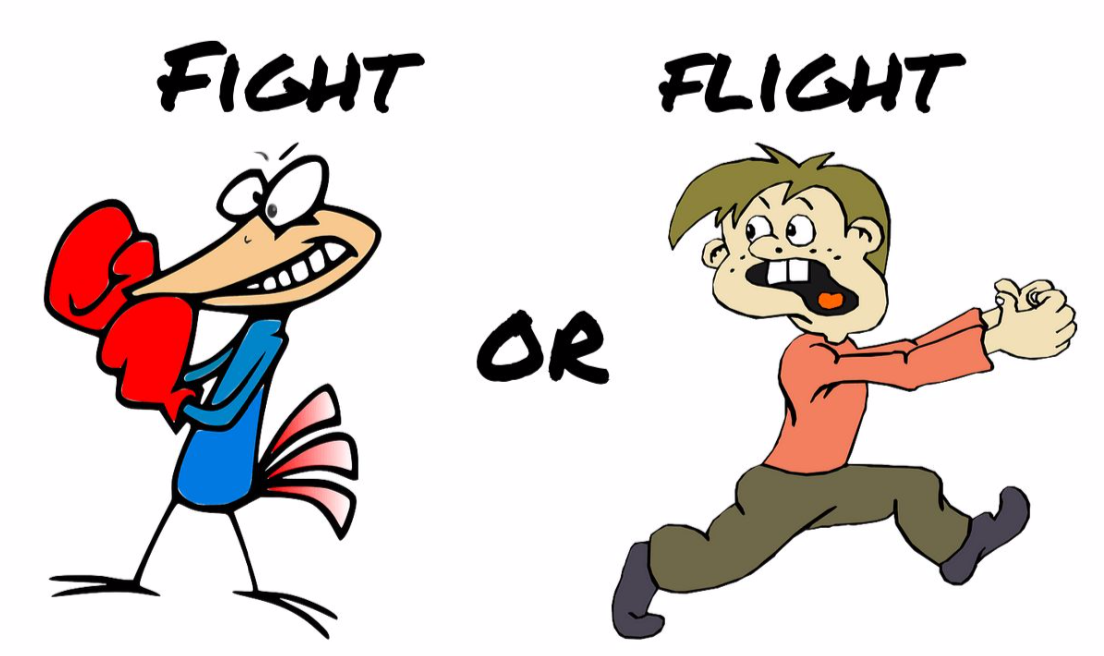
The primary function of our brain is to ensure our survival. When it comes to emotions and how we operate on a day to day basis, our brain comprises of 3 parts – the Neocortex (the thinking brain), the Limbic System (the feeling brain), and the Basal Ganglia (the reptilian brain). The Amygdala is the deepest and most critical part of the limbic system. It is most commonly activated when dealing with intense emotions. It triggers what is called the fight or flight response.
Research proves that when we are emotionally overwhelmed and experience a threat to our physical or psychological safety, our amygdala is triggered before our neocortex (the reasoning part of our brain) even knows about it. When this happens, the amygdala decides our behavior (the fight or flight response) and it is called an “Amygdala Hijack”.
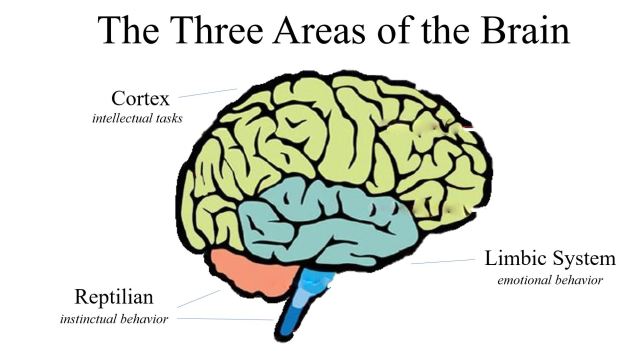
Anger Short Circuits Our Brain
This is what happens when we experience physical symptoms like a racing heart, sweating palms, or a shaking body — even in situations with no physical threat. Our ages-old survival mechanism kicks off and makes us react to things primitively before the rational brain has time to think things over.
This is one of the reasons emotions are good messengers but very bad masters. Our anger can tell us a lot about what we care about, but if we let it take over, it can short circuit the thinking part of our brain. When that happens, we react rather than respond to the situation.
“The truth will set you free, but first it will piss you off.” ― Joe Klaas
At the same time, just like any emotion anger can tell us a lot about ourselves. Anger has the power to clarify our thinking and reveal our moral lighthouses. But only if we are willing to listen. There are 3 ways we can use anger productively rather than let it destroy us and our relationships:-
1) Listening To Anger Reveals What We Care About
If we pause and reflect, anger can reveal what we deeply care about. For example – I once got angry at my manager. After reflection, I came to understand that the anger was not against the manager but against unfair behaviour. Once I realized that I was able to respond in a better way, and it revealed one of my deepest values to me – fairness and justice.
The more attention we pay, the more we can be aware of what our anger is trying to tell us. Anger can be our guiding light and a force to deploy ourselves in the world around us in a healthy and productive way rather than destructively. As I mentioned earlier anger is a secondary emotion. It hides many emotions behind it, but we can look deeper and figure out what those emotions are.
One way we can listen to what anger is trying to tell us is by separating facts from stories and assumptions which we might have made. Our minds can fool us easily. A thought comes into our mind after something happens, and we believe it to be true. In such moments, we can instead stop and validate each assumption which our mind is making before believing it. Whether it is true or not, or is it a story?
Anger can show us the way ahead, and what needs to change. Because anger tells us what is not okay, what we should not do, or that a deeper investigation is required, about something which is bothering us.
2) Anger Is An Opportunity To Practice Emotional Intelligence

In the heat of anger, we stop listening. We are only burning in rage. But after the immediate impulse of the anger is gone, it is an opportunity to practice emotional intelligence. And as with all skills. It gets better with practice and time.
Anger always comes along with a temptation to react. But seen another way, every time we get angry, it is an opportunity to express ourselves in a way that we can be proud of. Venting out in anger can certainly give us immediate relief, but we often end up damaging relationships and our reputation in the process. Not giving in to that impulse is an opportunity to practice emotional intelligence.
You might think that when angry, you can’t stop yourself from reacting. And this is why you hate being angry. But the truth is that anger is not the culprit here. Instead, it is you who lacks the ability to understand, reflect, and act responsibly in the face of your anger. Anger provides us with an opportunity to use the energy of our anger productively. When we do so, we strengthen relationships and build a strong reputation backed by responsible behaviour.
3) Anger is Love, and It Shows Your Commitment
We often get the most frustrated and angry at those whom we love or care deeply about. The opposite of love is not hate or anger, it is indifference. So when we see people in love fighting, it is not that the relationship is going downhill. Instead, it is a sign that the relationship has a lot of care and sincerity that is often expressed in anger. To expect anger to not arise in love is to not understand love at all.
You get angry because you care. You get angry because you love somebody, because you love a cause or because you love a certain value. You get angry because you want to reach an important goal or you see a possibility in the future. Something happened which violates that commitment you have to the person or to the cause or to the future goal. That is what makes you angry, and that is what we need to discover.
Have you noticed that when you are angry, you cannot think of anything else? It is because anger brings tremendous clarity with it, and forces you to focus on the current moment. If we can honor our anger instead of denying it, we can usee its energy. This energy arises because we feel vulnerable in love. If we can see it for what it is, we can use the force of anger to enrich the love which is at the root of anger in the first place.
Every time you are angry at someone you care about, take a moment to celebrate your commitment to the person or the relationship. Your response can change massively if you keep this commitment in mind in that moment of heat. Your anger is there to serve you and your relationships, but only if you are willing to pause and listen. You get angry because you love. Allow this love to strengthen the relationship rather than weaken it.
Conclusion
Understanding anger on a deeper level can be poetically beautiful. Once you learn to stop acting out impulsively and express your anger keeping love and care as the underlying commitment; you can channel it to nurture the relationship. We all feel anger, so in a way, anger connects us all. It is what makes us human.

This is enlightening… Poet beautiful and so true I m realising now. Thank you.
I love this article so much. It articulates things I feel in a wonderful way. I don’t trust people who say they don’t get angry. How can we not. It’s a great teacher . Our triggers are our friends. They teach us what we need to heal. I love that you connect anger to love. That has made a painful recent situation and many before make sense. Thankyou